When you create an algorithm, a Git repository is initialized to store its source code. Algorithmia supports hosting that repository within the Algorithmia platform itself or using one of a number of external source code management (SCM) providers, listed below. In this guide, we’ll walk through the following:
Using an OAuth-based SCM provider
- Hosting source code on Algorithmia
- Hosting source code on GitHub
- Hosting source code on Bitbucket Cloud
- Hosting source code on GitLab
Using a non-OAuth based SCM provider
Enterprise Users: By default, on new Algorithmia clusters algorithm source code can only be hosted internally within the Algorithmia platform. Please consult your cluster administrator to have them create an external SCM configuration.
If you haven’t used Git before, we recommend this Git tutorial series by GitHub. You don’t need to know how to use Git to get started on Algorithmia. However, we recommend having at least a basic familiarity with it, as it’s a powerful and widely used collaboration tool and is required to use some of our more advanced functionality.
Choosing a repository host
Before we dive into the repository hosts Algorithmia supports, let’s discuss the various use cases that best fit each type.
If you’re just getting started with Algorithmia, or you want to leverage Algorithmia’s built-in Web IDE, you should choose Algorithmia as your repository host. This is the simplest way to get started with the platform, but presents limitations when it comes to using external collaboration tools.
If you want to easily share source code with your colleagues and to use best practices like code reviews, we recommend an external repository host. This does mean that our browser-based Web IDE won’t be available for use, but the configuration will allow you to more flexibly manage access to your source code and integrate with any existing SCM workflows you may use.
Algorithm Migration: At this time, Algorithmia does not have built-in support for migrating algorithms between repository hosts. However, to achieve the same end result, you can create a new algorithm with its code hosted by the target SCM provider and then migrate your algorithm source code from the original algorithm to the new one.
Hosting source code on Algorithmia
Hosting your algorithm’s source code within the Algorithmia platform is simple, and no special configuration is required. When creating your algorithm, simply select “Algorithmia” as the “repository host” within the source code configuration section.
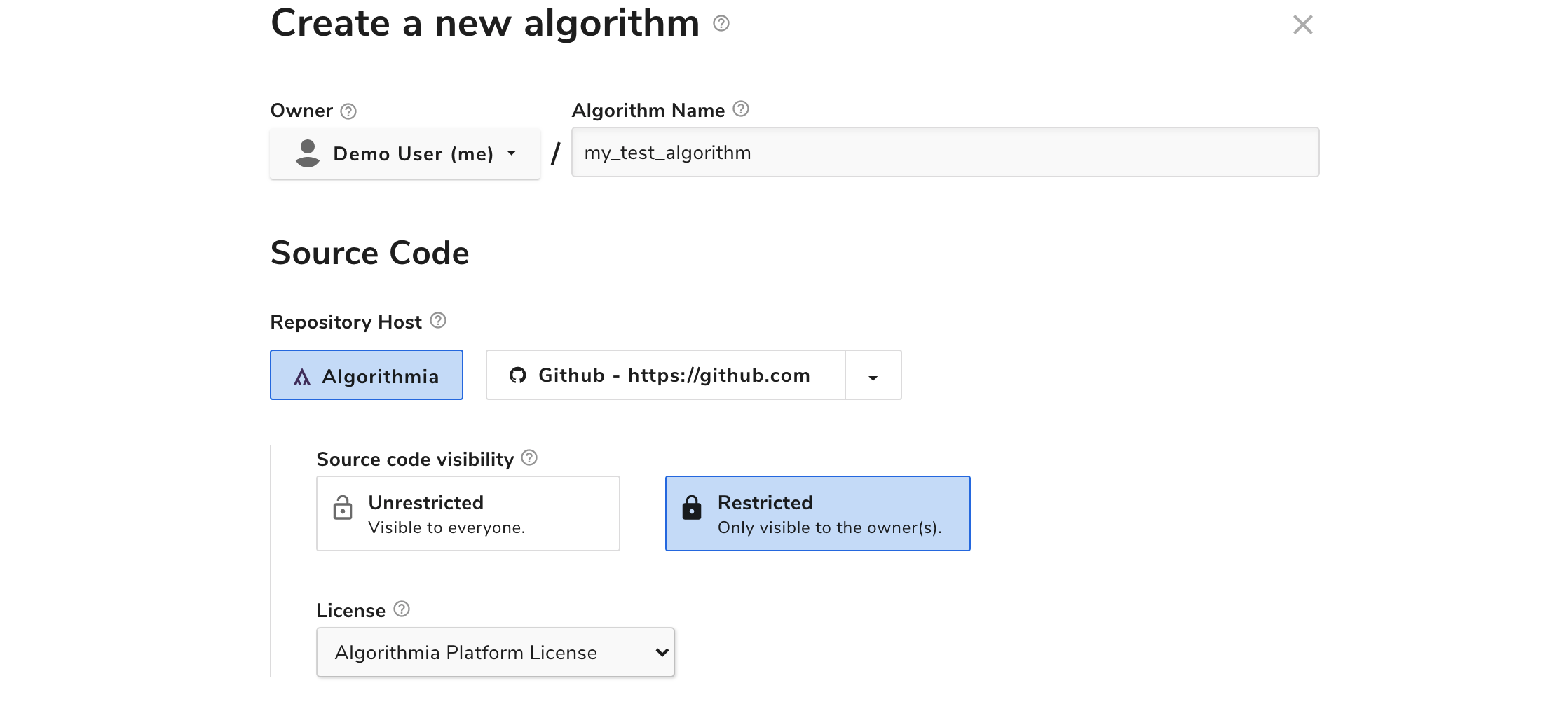
The “source visibility” setting determines whether the source code for your algorithm will be viewable from other accounts on the cluster. Select “restricted” if you’d only like algorithm owners to have access to the algorithm’s source code.
Editing source code locally
When your algorithm is created, our platform generates a unique HTTPS URL you can use to clone your algorithm’s Git repository.
git clone https://git.CLUSTER_DOMAIN/git/ALGO_OWNER/ALGO_NAME.gitFor your algorithm, you’ll replace the ALGO_OWNER and ALGO_NAME values with the name of your account and the name of the algorithm, respectively. For non-enterprise customers, CLUSTER_DOMAIN will be algorithmia.com; enterprise customers must replace this value with their cluster-specific domain name string.
If you’ve never cloned algorithm code before, you’ll be asked to provide your Algorithmia account name and password to authenticate to the platform.
Enterprise Users: If your Algorithmia instance is configured to use OIDC, you won’t have a password. To obtain a password, navigate to your account settings page and click “Regenerate Account Password”. Follow the instructions to obtain a password you can use to authenticate with your Algorithmia-hosted Git repositories.
Make any source code modifications you’d like and commit them to your repository’s master branch.
git add FILE_TO_COMMIT
git commit -m "Message about commit changes"Finally, push your changes to Algorithmia; this will trigger a new algorithm build. Note that Algorithmia will only compile the head of the master branch on each push. It won’t compile intermediate commits, so they’ll all be squashed together into the one build.
git push origin masterNote that attempts to rewrite the history of an algorithm’s source code repository will be rejected, as doing so could potentially break prior versions of the algorithm.
SSH Support: Algorithmia doesn’t currently support SSH as a means of cloning algorithm repositories.
Editing source code in the Algorithmia Web IDE
Algorithms whose source code is hosted within Algorithmia can be edited directly through our Web IDE. To access the Web IDE for algorithms you own or have access to through membership in the algorithm-owning organization, click on the “Source Code” tab on an algorithm’s homepage.
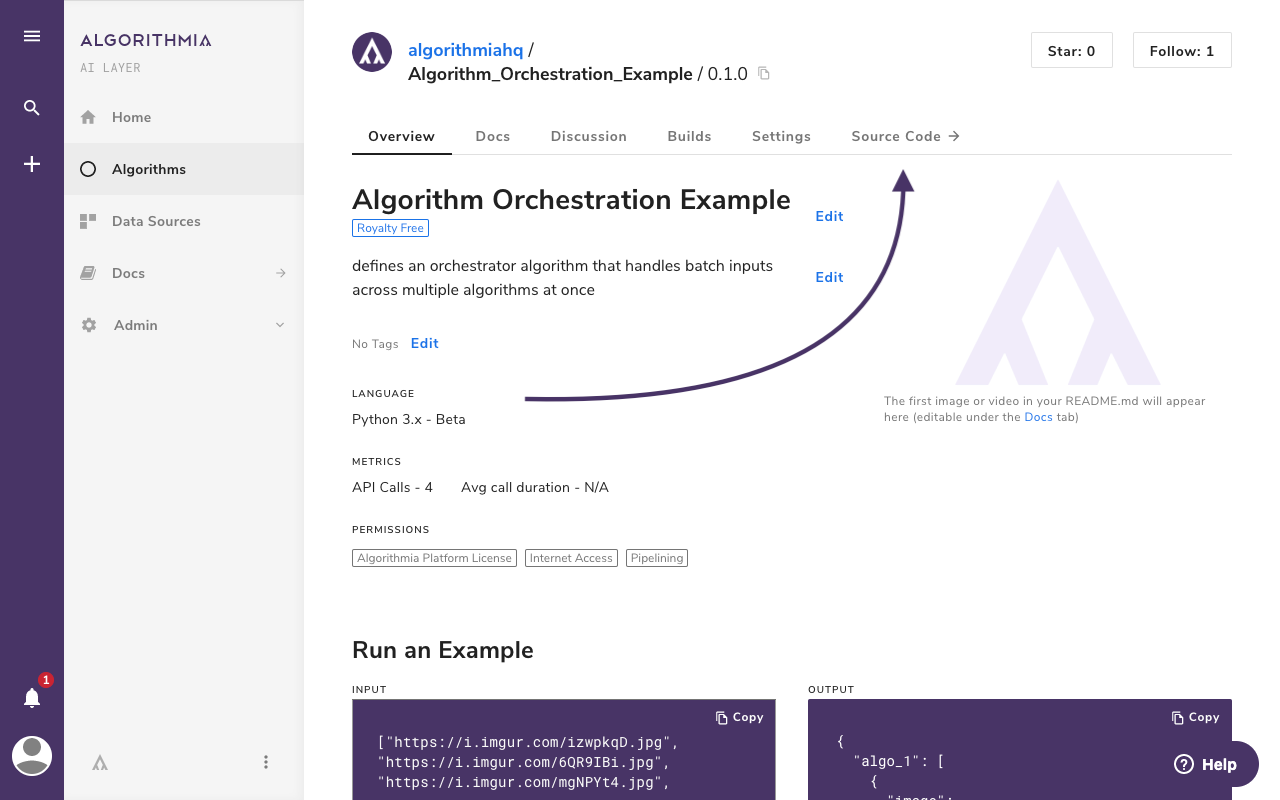
In the Web IDE, you can create, modify, and delete algorithm files.
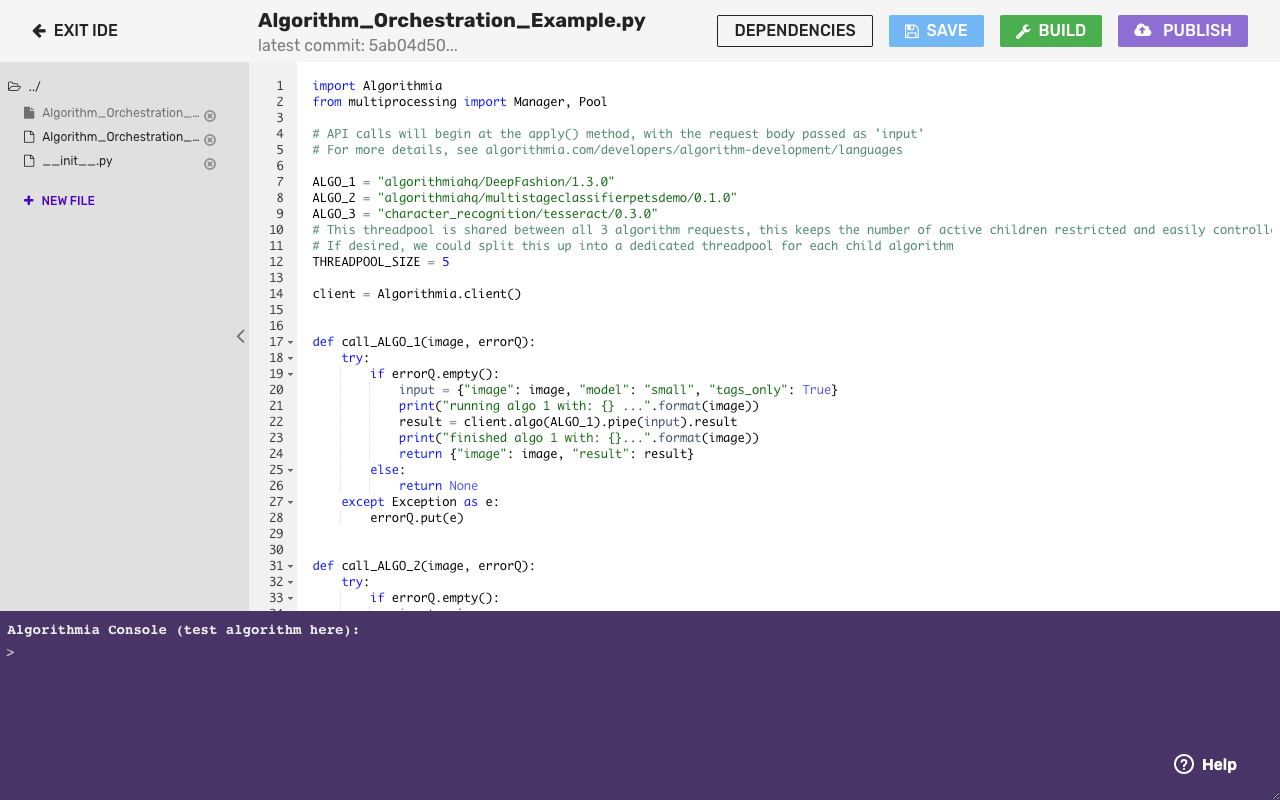
Once you’re satisfied with your changes, click the “Build” button, optionally test your changes in the test console at the bottom, and click “Publish” to create a new version of the algorithm.
Hosting source code on GitHub
By hosting your algorithm’s source code on GitHub, you can take advantage of GitHub’s rich set of developer features, such as pull requests and GitHub Actions, and also ensure that access to your source code is carefully mediated. We support both GitHub and GitHub Enterprise; we use the term “GitHub” to refer to both products, as the configuration and usage is the same.
If you haven’t used Git before, we recommend this Git tutorial series by GitHub.
Web IDE Support: At this time we don’t support editing source code in our Web IDE for GitHub-hosted algorithms.
Enterprise Users: By default, on new Algorithmia clusters algorithm source code can only be hosted internally within the Algorithmia platform. As such, you won’t see GitHub listed as a repository host for new algorithms until your cluster administrator creates a GitHub configuration.
Creating GitHub-hosted algorithms
To create an algorithm with its source code hosted on GitHub, simply select any available GitHub SCM configuration for “repository host” in the modal.
The first time you create a GitHub-hosted algorithm, you’ll be prompted to connect your GitHub account. Click “Authorize” and follow the instructions in the pop-op window to give Algorithmia permission to create and manage Git repositories on your behalf. Once you’ve connected your GitHub account to Algorithmia, you’ll be able to select any available GitHub configuration to host your source code repository when you create a new algorithm.
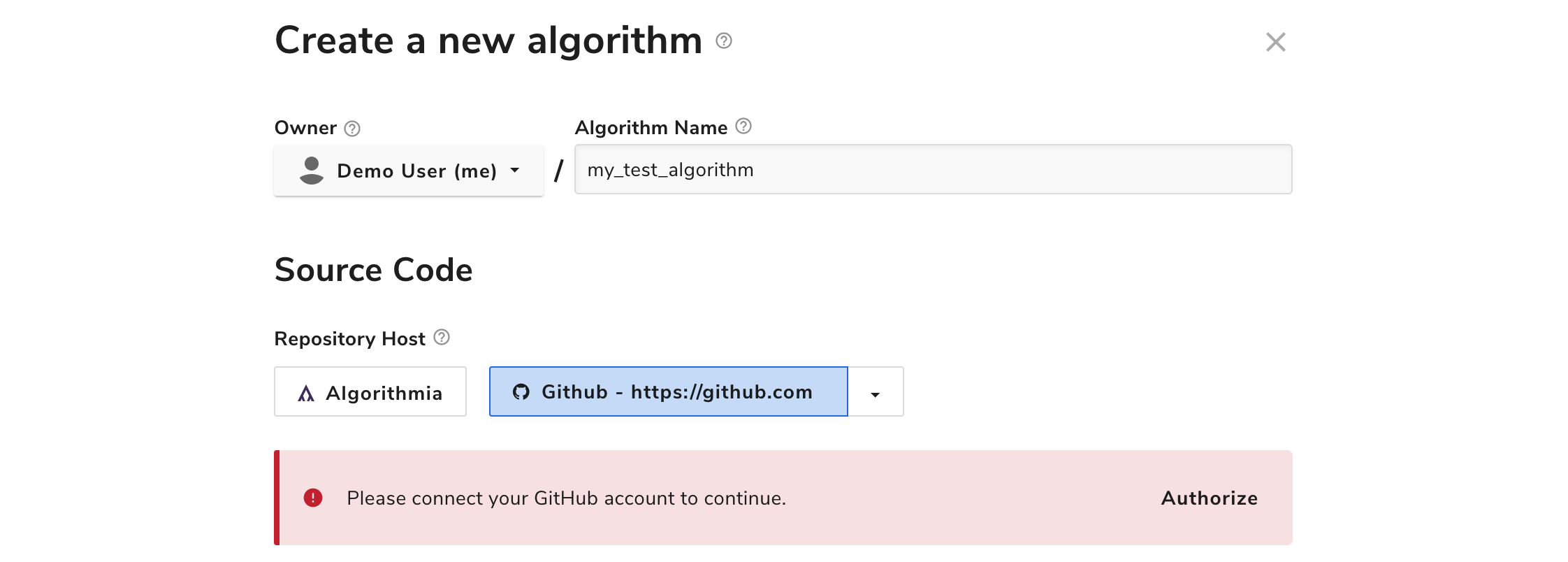
You can customize two aspects of any GitHub repository that’s created for an algorithm: the repository’s owner, and its name.
By default, all GitHub repositories are created under your personal GitHub account. However, you may optionally choose to host your code under any GitHub organizations of which you’re a member, as long as they’ve been configured by your cluster administrator. The available organizations are listed in the “repository owner” drop-down.
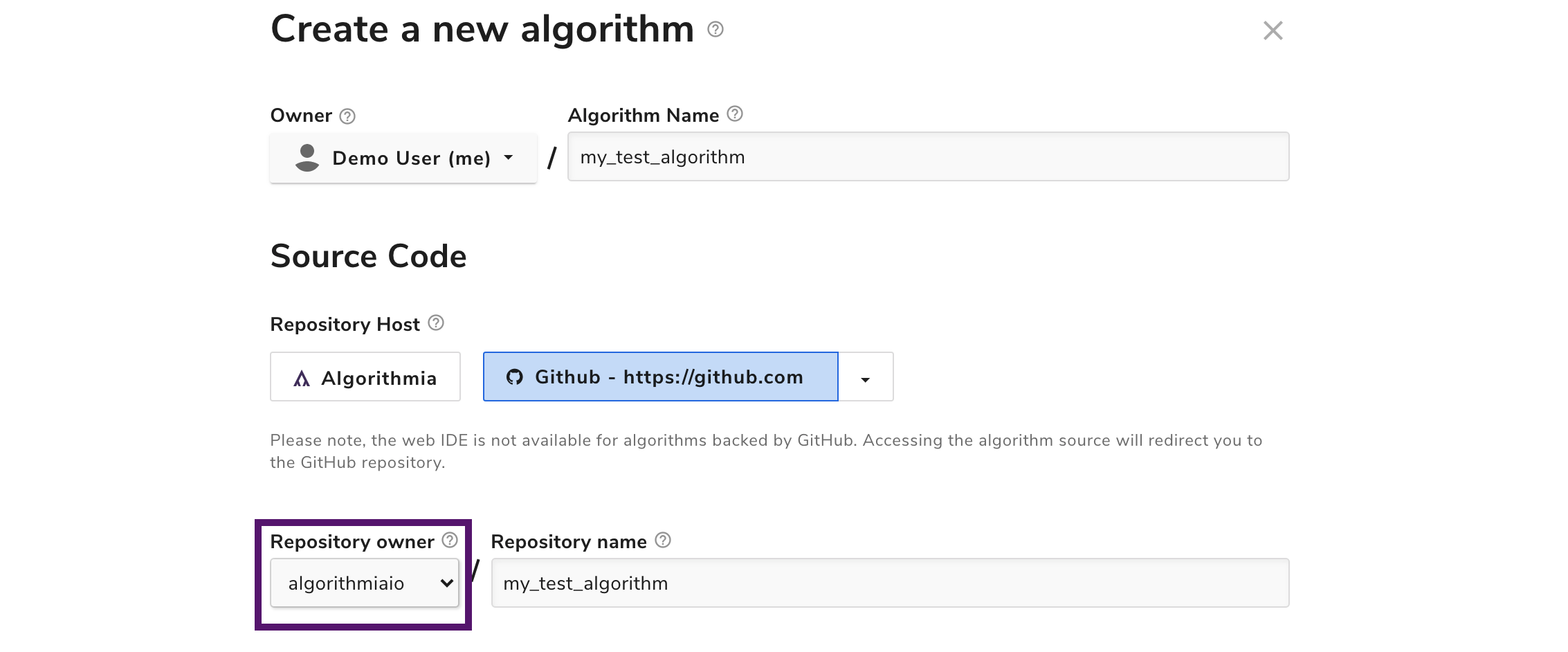
You may also customize the name of the repository that’s created. By default, it’ll be the name of your algorithm.
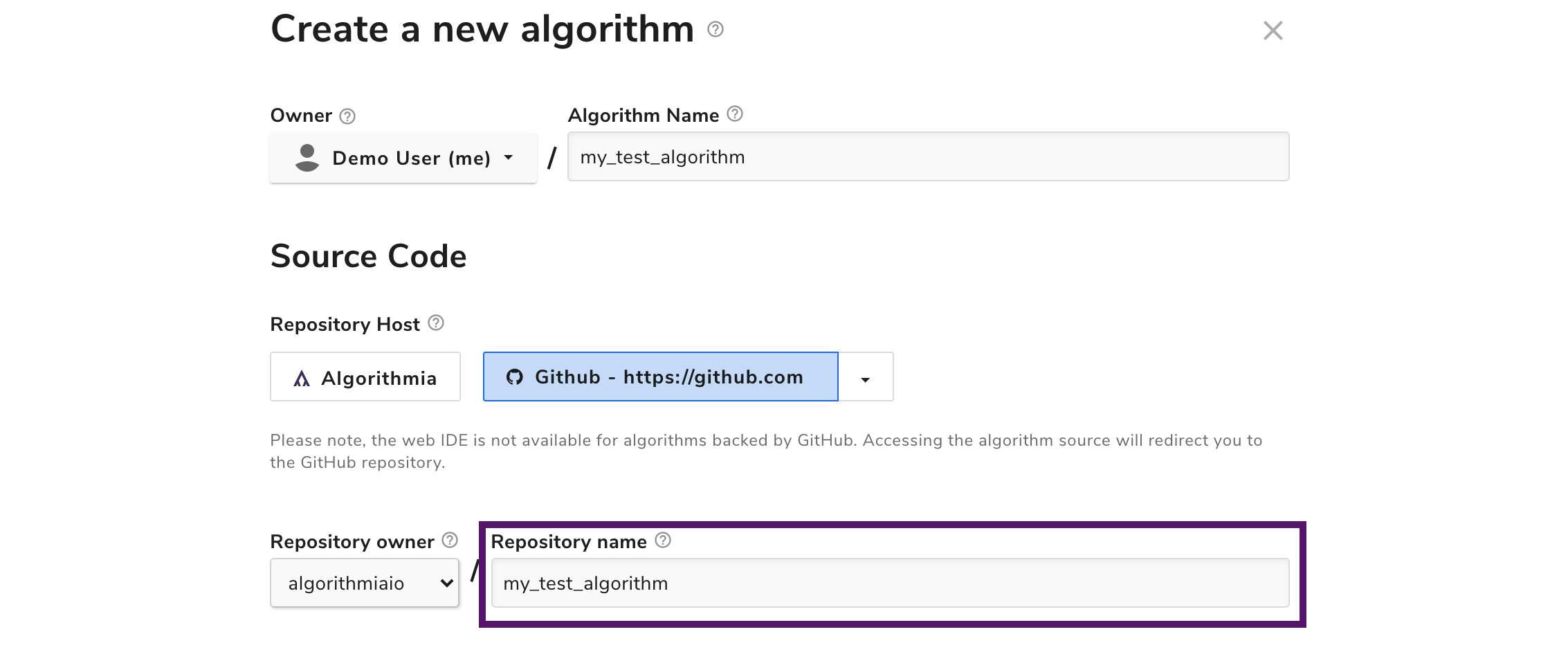
If you decide to use an alternative name, we recommend you use only letters, numbers, hyphens, and/or underscores. While GitHub will accept characters outside this range, it will replace any unsupported characters with an underscore, potentially resulting in an undesired repository name.
When we create your repository, we associate the following with it:
- A deploy key: GitHub deploy keys allow read-only access to specific repositories, and are GitHub’s prescribed means by which external services can fetch code for building and deploying. These keys are not tied to individual permissions, and as such will allow Algorithmia to continue building an algorithm even if the permissions of the creating user change. We also use deploy keys to obtain your repository’s commit log (to display changes when publishing versions) and README.md (for use as algorithm documentation).
- Webhooks: We set up webhooks to receive notifications about changes to your repository, such as when there’s a change to its default branch.
Updating GitHub-hosted algorithms
Once you’ve created your algorithm, any commits to your GitHub repository’s default branch will result in a build on Algorithmia. At creation, your repository’s default branch will be the main branch, but you can change this at any time within GitHub. In your repository, click “Settings” and then “Branches” on the left side.
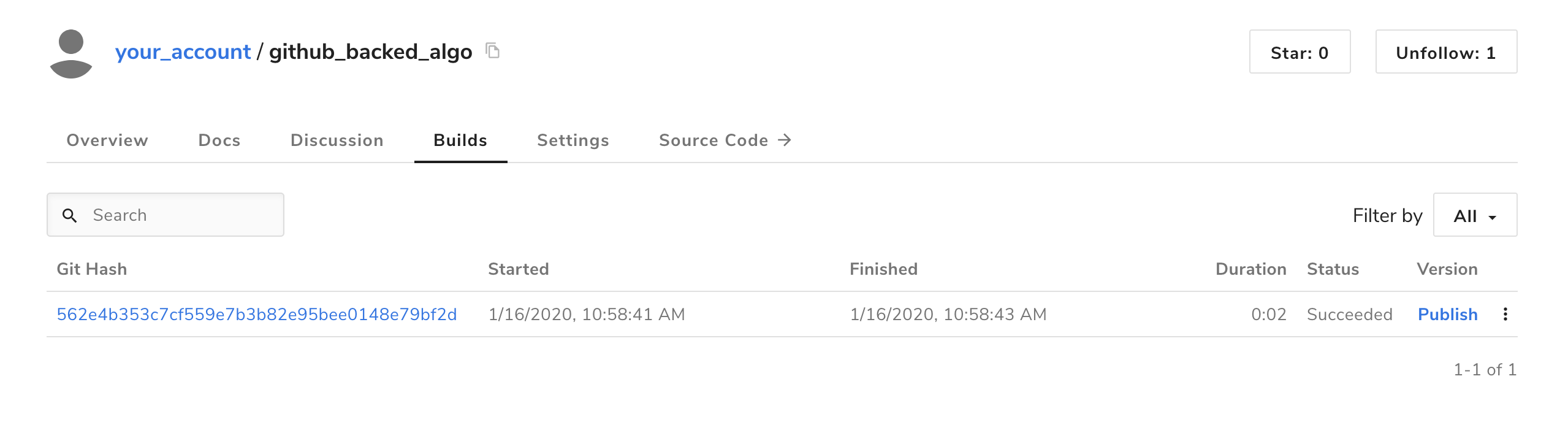
For algorithms you own and for those owned by organizations of which you’re a member, you can view builds on the algorithm homepage under the “Builds” tab.
Publishing GitHub-hosted Algorithms
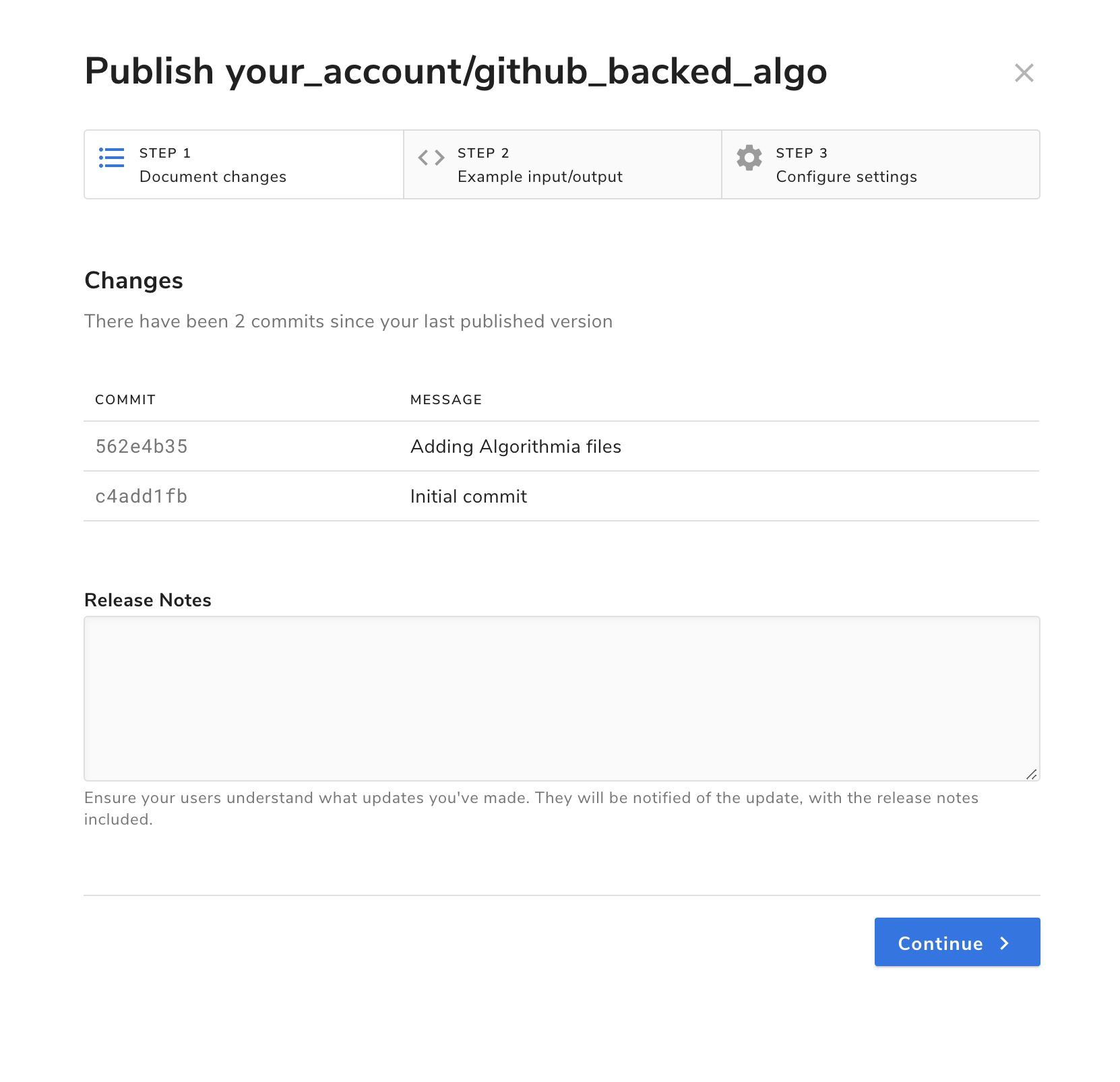
When you’re ready to create a new version of your algorithm, visit the algorithm’s homepage and select the “Builds” tab. Locate the build corresponding to the specific commit SHA you wish to use, and then click “Publish” on the right side of the row.
This will open a modal where you can enter release notes and version information before publishing your algorithm.
If you don’t see any builds listed, make sure that you’re pushing commits to your repository’s default branch, because builds are only triggered for commits to this branch.
To learn more about algorithm builds, click here.
Deleting GitHub-hosted algorithms
If you wish to delete an algorithm whose source code is hosted on GitHub, have no fear—the repository will be left unharmed. If you do wish to destroy your algorithm’s source code, you can follow these instructions.
Managing your GitHub authorization
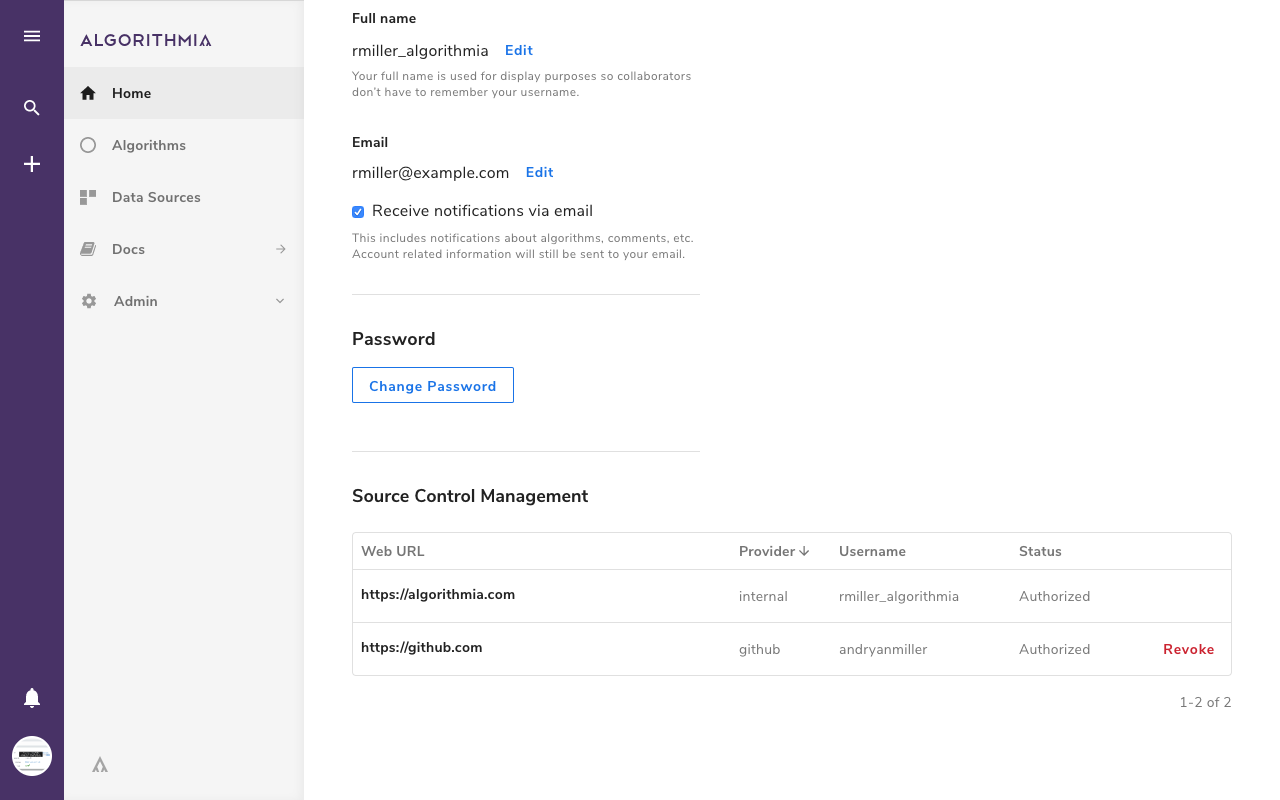
If you want to review your GitHub authorization status, you can visit your account settings page. Simply scroll to the “Source Code Management” section to view any prior GitHub authorizations, or to connect your account.
Troubleshooting GitHub-hosted algorithms
If we experience a temporary disruption in connectivity with GitHub, your source code will be unavailable for modification during the duration of that disruption. The following are some additional scenarios under which algorithm source code won’t be available, to help you troubleshoot.
Your repository’s deploy key was removed
We depend on deploy keys to pull source code from your algorithm for building. A deploy key is simply an SSH keypair with read-only access to a specific repository. Algorithmia securely stores the private key while the public key is shared with GitHub.
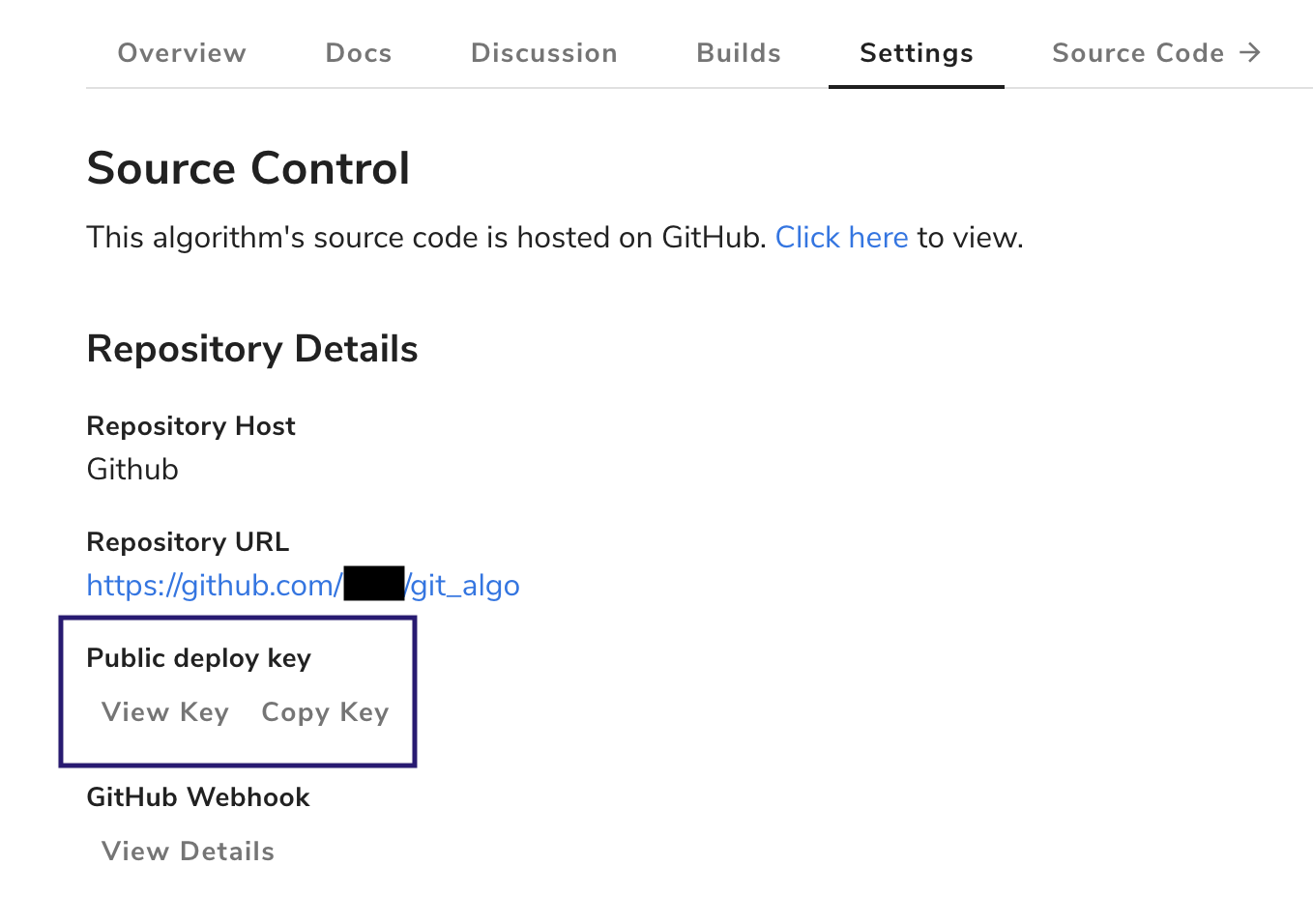
You can obtain the public key for your repository by navigating to your algorithm’s settings page and clicking “View Key”:
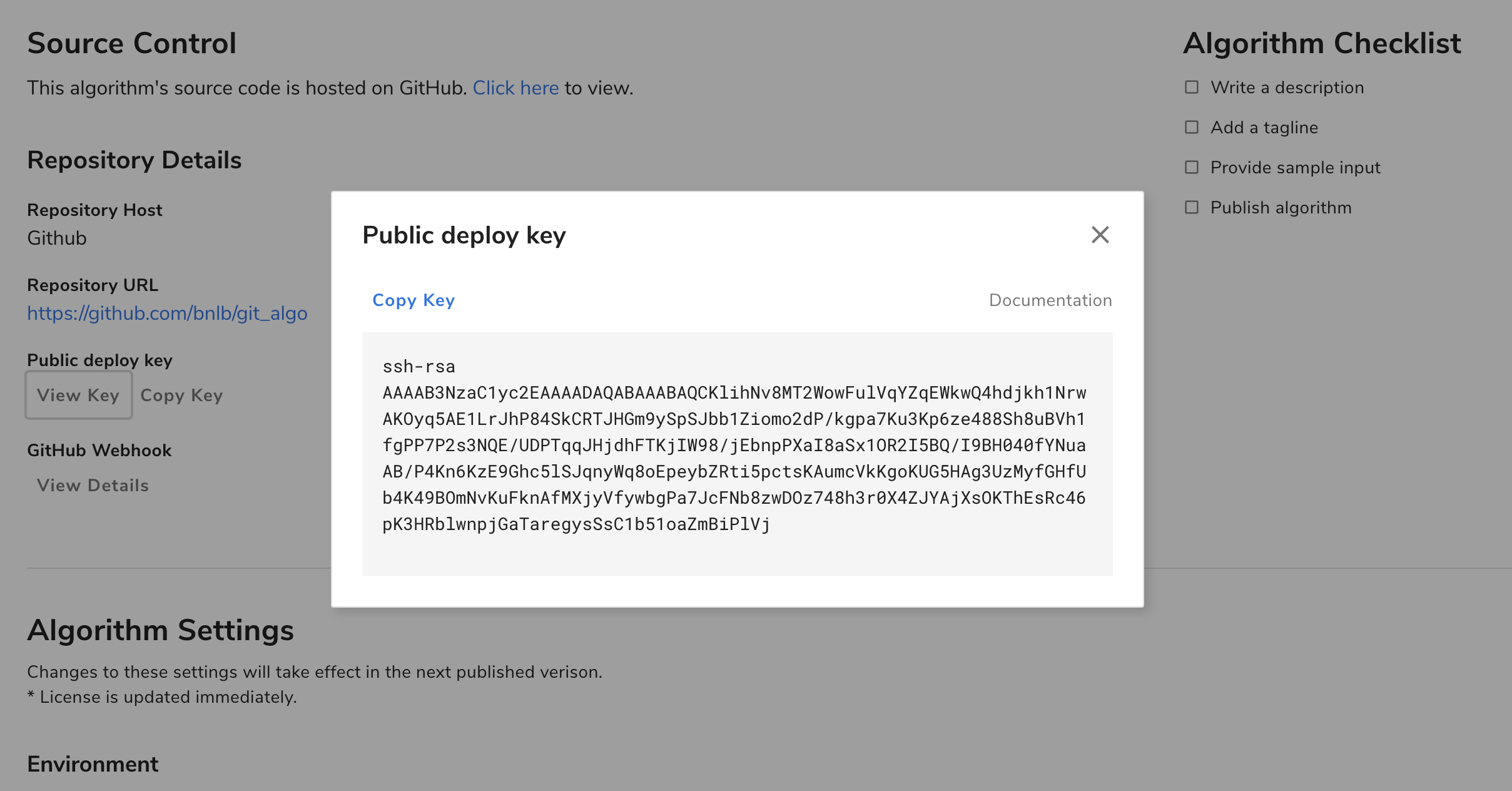
You’ll be presented with a modal, from which you can copy the public key.
With the deploy key in hand, simply follow instructions outlined here to restore the public key to your repository.
Your repository was deleted
If your algorithm’s GitHub repository was deleted, you may attempt to restore the relevant repository. It’s essential that both the repository’s deploy key and webhooks remain in place after restoration, otherwise we won’t be able to pull your source code, or know when you make changes.
Your repository’s webhook needs to be restored
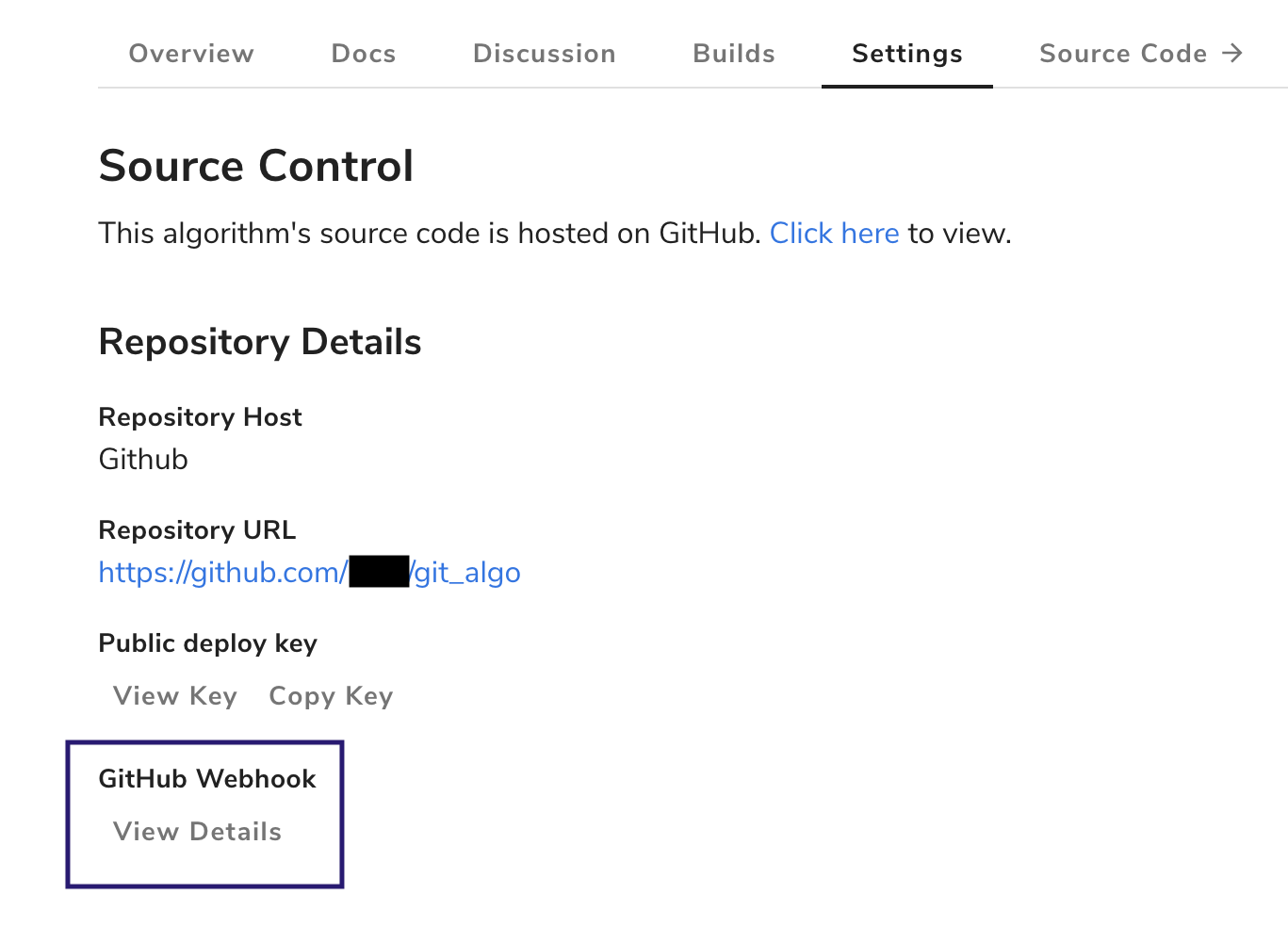
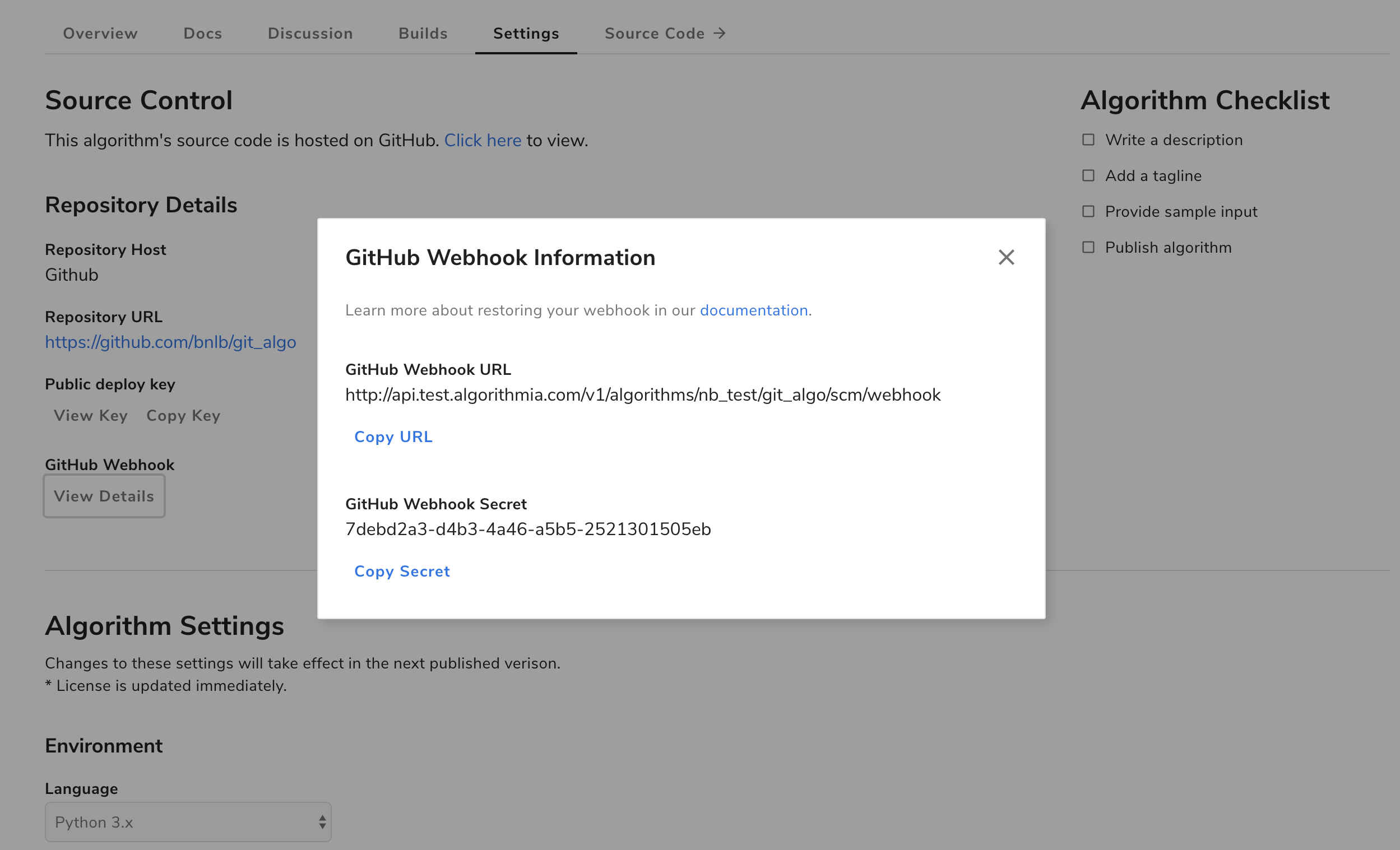
We depend on webhooks to notify us when changes have occurred to your algorithm’s repository. To restore your webhook within GitHub, first locate the webhook URL and secret. This can be found under “Settings” on your algorithm’s homepage in Algorithmia. Just click “View Details” under “GitHub Webhook”.
You’ll then be presented with a modal, from which you can copy the webhook URL and secret.
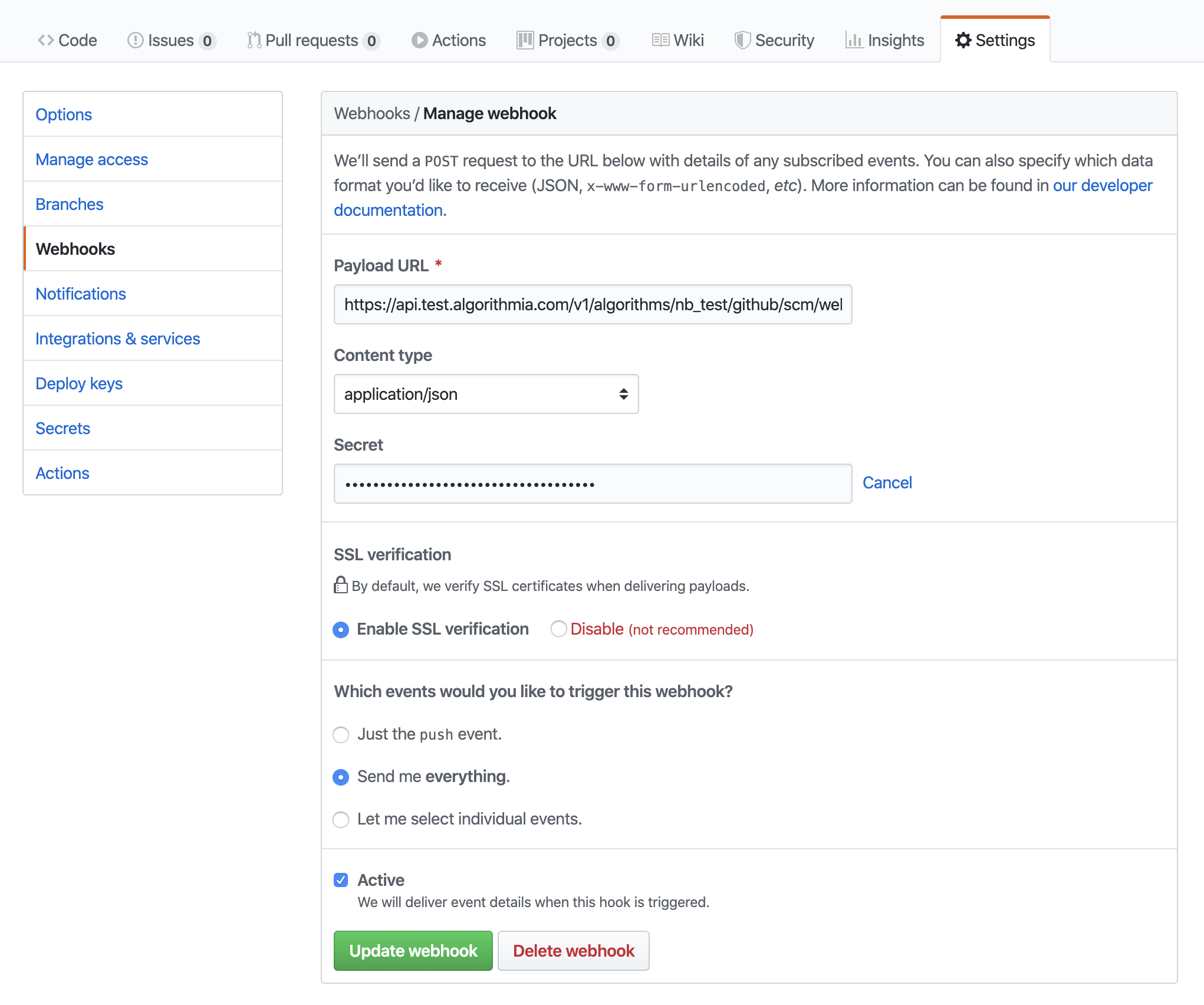
Once you’ve located these values, visit your algorithm’s repository on GitHub and click on the “Settings” tab. Click “Webhooks” on the left side, and you’ll be able to restore your webhook by entering the webhook URL and secret.
FAQ
I’d like to reuse an existing GitHub repository for my algorithm. Is this possible?
At this time we’re only able to use new, purpose-created repositories for GitHub-backed algorithms, which Algorithmia itself creates and provisions.
Can I rename or move the GitHub repository that backs my algorithm?
Yes! Upon any change to your repository’s name or owner we receive a webhook which we use to update our system to point to the new repository address.
I’m a member of a GitHub organization, but I don’t see that organization listed as a possible owner when creating an algorithm. What’s wrong?
On the Algorithmia side, a cluster administrator must first create a configuration to the GitHub account. If this has been done and the issue persists, an administrator of your GitHub organization likely needs to approve the OAuth application that’s being used to authorize Algorithmia users. You can request approval by following the instructions in this GitHub documentation.
I revoked access to the Algorithmia’s Github OAuth application, and now none of the repositories I created can build!
When you revoke access to an OAuth app, Github automatically revokes both your token and any deploy keys you may have created via the OAuth app. To fix your algorithms, simply follow the instructions above on restoring a deploy key to a repository.
Hosting source code on Bitbucket Cloud
By hosting your algorithm’s source code on Bitbucket Cloud, you can take advantage of Bitbucket Cloud’s rich set of developer features, such as pull requests, and also ensure that access to your source code is carefully mediated.
If you haven’t used Git before, we recommend this Git tutorial series by GitHub.
Web IDE Support: At this time we don’t support editing source code in our Web IDE for BitBucket Cloud-hosted algorithms.
Enterprise Users: By default, on new Algorithmia clusters algorithm source code can only be hosted internally within the Algorithmia platform. As such, you won’t see Bitbucket Cloud listed as a repository host for new algorithms until your cluster administrator creates a Bitbucket Cloud configuration.
Creating Bitbucket Cloud-hosted algorithms
To create an algorithm with its source code hosted on Bitbucket Cloud, simply select any available Bitbucket Cloud SCM configuration for “repository host” in the modal.
The first time you create a Bitbucket Cloud-hosted algorithm, you’ll be prompted to connect your Bitbucket Cloud account. Click “Authorize” and follow the instructions in the pop-op window to give Algorithmia permission to create and manage Git repositories on your behalf. Once you’ve connected your Bitbucket Cloud account to Algorithmia, you’ll be able to select any available Bitbucket Cloud configuration to host your source code repository when you create a new algorithm.
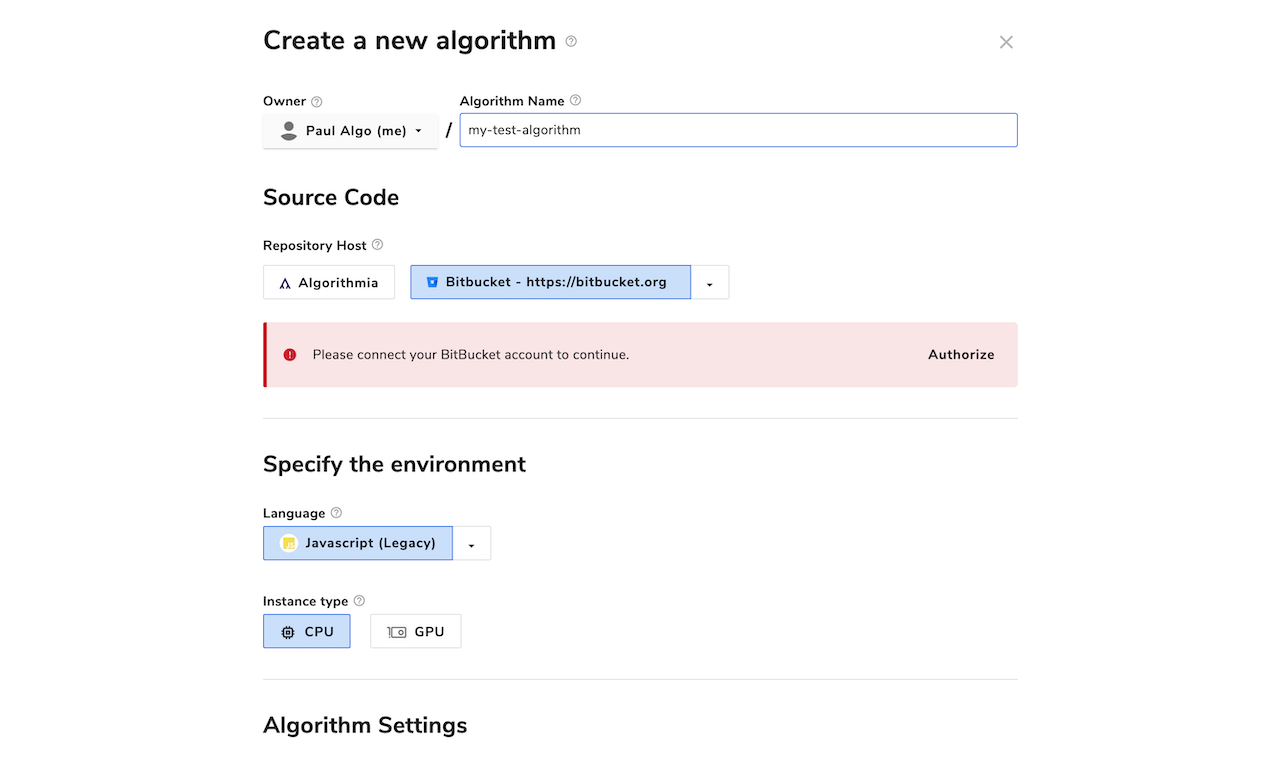
You can customize two aspects of any Bitbucket Cloud repository that’s created for an algorithm: the repository’s owner, and its name.
By default, all Bitbucket Cloud repositories are created under your personal Bitbucket Cloud account. However, you may optionally choose to create repositories under any Bitbucket Cloud organizations of which you’re a member, as long as they’ve been configured by your cluster administrator. The available organizations are listed in the “repository owner” drop-down:
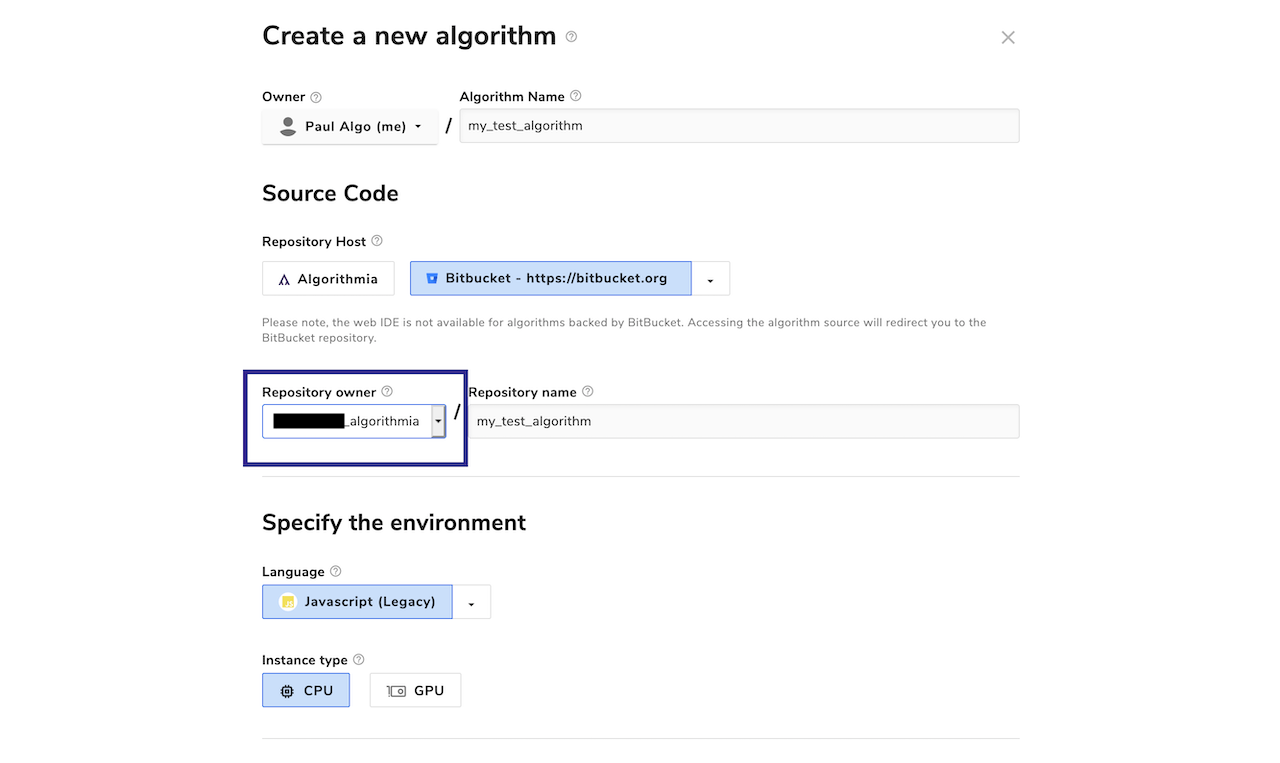
You may also customize the name of the repository that’s created. By default, it’ll be the name of your algorithm.
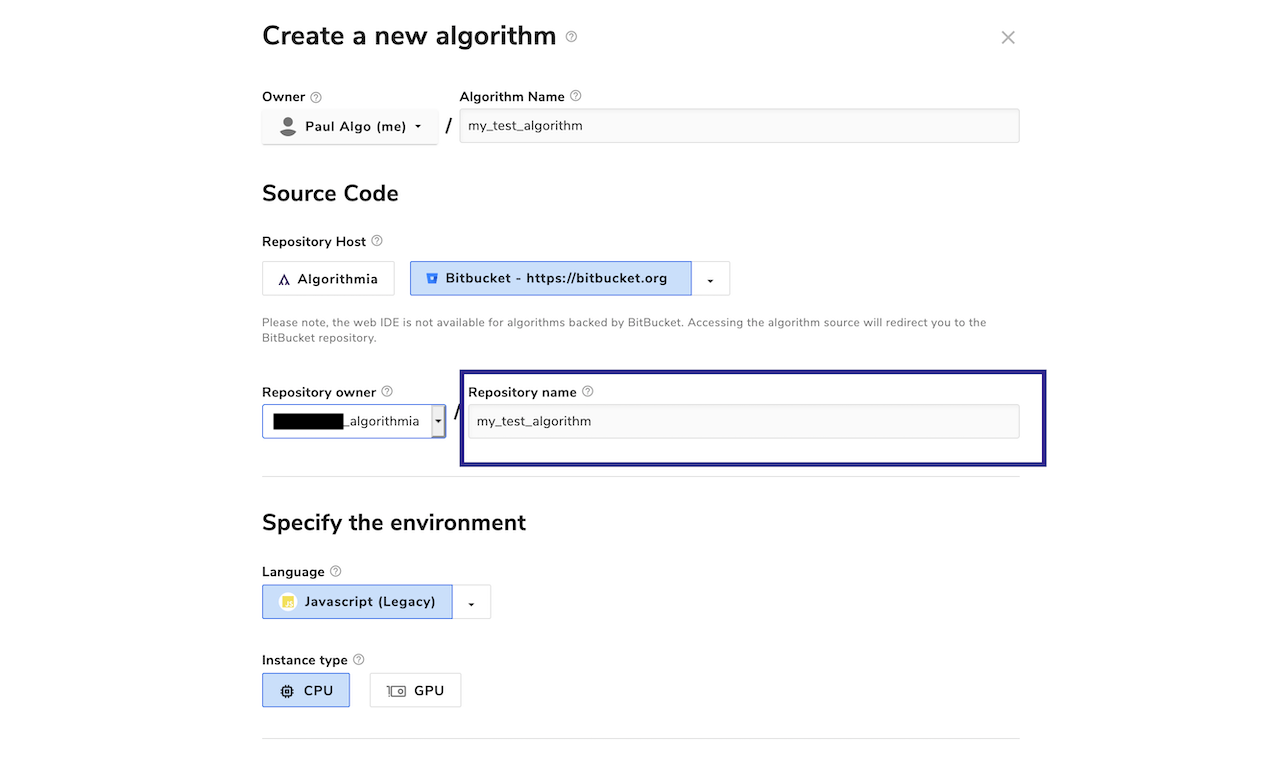
If you decide to use an alternative name, we recommend that you use only letters, numbers, hyphens, and/or underscores. While Bitbucket Cloud will accept characters outside this range, it will replace any unsupported characters with an underscore, potentially resulting in an undesired repository name.
When we create your repository, we associate the following with it:
- An access key: Bitbucket Cloud access keys allow read-only access to specific repositories, and are Bitbucket Cloud’s prescribed means by which external services can fetch code for building and deploying. These keys are not tied to individual permissions, and as such will allow Algorithmia to continue building an algorithm even if the permissions of the creating user change. We also use access keys to obtain your repository’s commit log (to display changes when publishing versions) and README.md (for use as algorithm documentation).
- Webhooks: We set up webhooks to receive notifications about changes to your repo, such as when there’s a change to its default branch.
Updating Bitbucket Cloud-hosted algorithms
Once you’ve created your algorithm, any commits to your Bitbucket Cloud repository’s default branch will result in a build on Algorithmia. At creation, your repository’s default branch will be your master branch, but you can change this at any time in your repository’s settings.
You can view your algorithm’s builds by heading to its landing page and clicking the “Builds” tab if you are the algorithm’s owner.
Publishing Bitbucket Cloud-hosted algorithms
When you’re ready to create a new version of your algorithm, visit that algorithm’s page and select the “Builds” tab. Locate the build corresponding to specific commit SHA you wish to use, and then click “Publish” on the right side of the row.
This will open a publish modal that will let you publish your algorithm.
If you don’t see any builds listed, make sure that you’re pushing commits to your repository’s default branch. Builds are only triggered for commits pushed to the default branch.
To learn more about algorithm builds, click here.
Deleting Bitbucket Cloud-hosted algorithms
If you wish to delete an algorithm that hosts its source code on Bitbucket Cloud, have no fear—the repository will be left unharmed. If you do wish to destroy your algorithm’s source code, you can follow these instructions.
Managing your Bitbucket Cloud authorization
If you want to review your Bitbucket Cloud authorization status, you can visit your account settings page. Simply scroll to the “Source Code Management” section to view any prior Bitbucket Cloud authorizations, or to connect your account.
Troubleshooting Bitbucket Cloud-hosted algorithms
If we experience a temporary disruption in connectivity with Bitbucket Cloud, your source code will be unavailable for modification during the duration of that disruption. The following are some additional scenarios under which algorithm source code won’t be available, to help you troubleshoot.
Your repository’s access key was removed
We depend on access keys to pull source code from your algorithm for building. An access key is simply an SSH keypair with read-only access to a specific repository. Algorithmia securely stores the private key while the public key is shared with Bitbucket Cloud.
You can obtain the public key for your repository by navigating to your algorithm’s settings page and clicking “View Key”. You’ll then be presented with a modal, from which you can copy the public key.
With the access key in hand, simply follow instructions outlined here to restore the public key to your repository.
Your repository was deleted
If your algorithm’s Bitbucket Cloud repository was deleted, Bitbucket Cloud does not have a mechanism for restoring. It is essential that both the repository’s access key and webhooks remain in place, otherwise we will not be able to pull your source code, or know when you make changes.
Your repository’s webhook needs to be restored
We depend on webhooks to notify us of changes to your algorithm’s repository. To restore your webhook within Bitbucket Cloud, first locate the webhook URL. This can be found under the “Settings” tab on your algorithm’s homepage in Algorithmia. Just click “View Details” under “Bitbucket Cloud Webhook”.
You’ll then be presented with a modal, from which you can copy the webhook URL.
Once you’ve found this value, visit your algorithm’s repository on Bitbucket Cloud and click on the Settings tab. Click ‘Webhooks’ on the left side, and you’ll be able to restore your webhook by entering the webhook URL.
FAQ
I’d like to reuse an existing Bitbucket Cloud repository for my algorithm. Is this possible?
At this time we are only able to use new, purpose-created repositories for Bitbucket Cloud-backed algorithms, which Algorithmia itself creates and provisions.
Can I rename or move the Bitbucket Cloud repository that backs my algorithm?
Yes! Upon any change to your repository’s name or owner we receive a webhook which we will use to update our system to point to the new repository address.
I revoked access to the Algorithmia’s Bitbucket Cloud OAuth application, and now none of the repositories I created can build!
When you revoke access to an OAuth app, Bitbucket Cloud automatically revokes both your token and any access keys you may have created via the OAuth app. To fix your algorithms, simply follow the instructions above on restoring access keys to a repository.
Hosting source code on GitLab
By hosting your algorithm’s source code on GitLab, you can take advantage of GitLab’s rich set of developer features, such as pull requests and GitLab CI/CD, and also ensure that access to your source code is carefully mediated.
If you haven’t used Git before, we recommend this Git tutorial series by GitHub.
Web IDE Support: At this time we don’t support editing source code in our Web IDE for GitLab-hosted algorithms.
Enterprise Users: By default, on new Algorithmia clusters algorithm source code can only be hosted internally within the Algorithmia platform. As such, you won’t see GitLab listed as a repository host for new algorithms until your cluster administrator creates a GitLab configuration.
Creating GitLab-hosted algorithms
To create an algorithm with its source code hosted on GitLab, simply select any available GitLab SCM configuration for “repository host” in the modal.
The first time you create a GitLab-hosted algorithm, you’ll be prompted to connect your GitLab account. Click “Authorize” and follow the instructions in the pop-op window to give Algorithmia permission to create and manage Git repositories on your behalf. Once you’ve connected your GitLab account to Algorithmia, you’ll be able to select any available GitLab configuration to host your source code repository when you create a new algorithm.
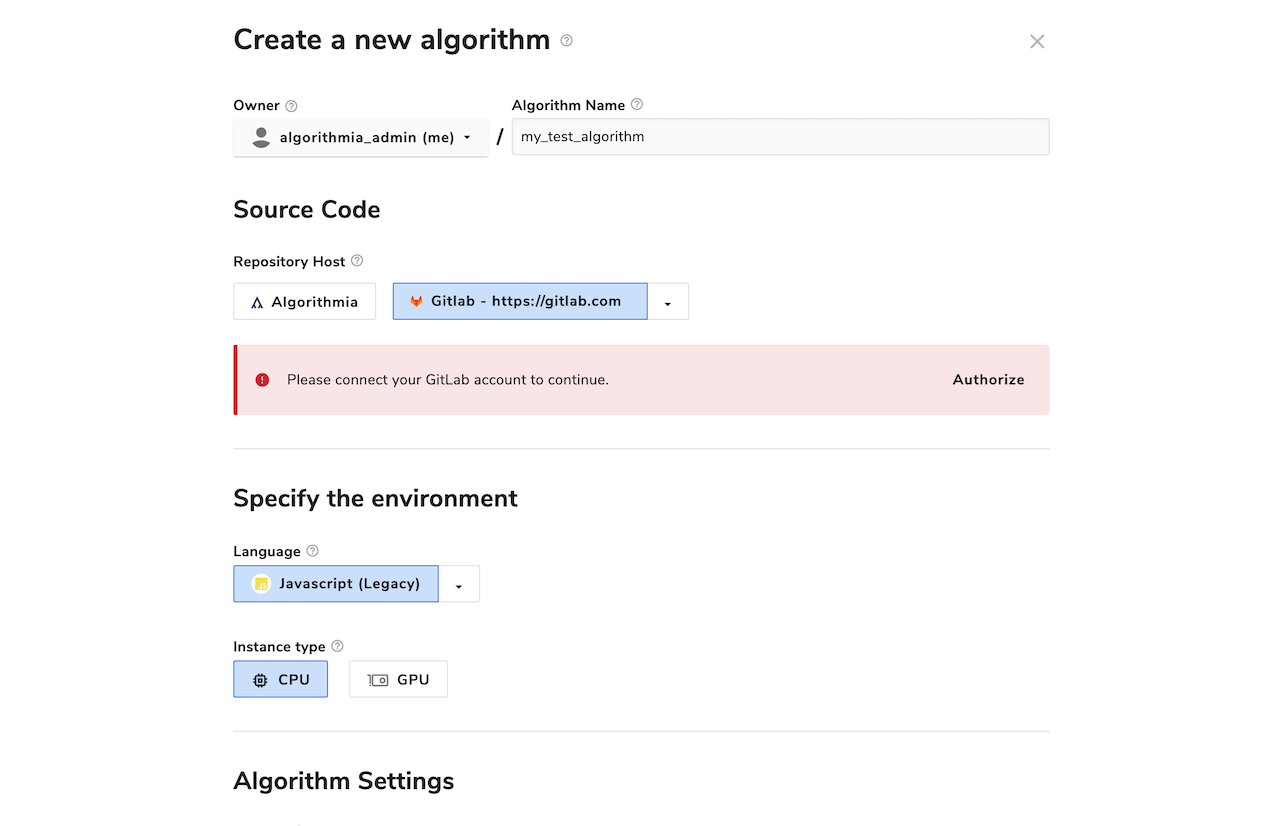
You can customize two aspects of the GitLab repositories that are created for your algorithms: the repository’s owner, and its name.
By default, all GitLab respositories are created under your personal GitLab account. However, you may optionally choose any GitLab organizations of which you’re a member, as long as they’ve been configured by your cluster administrator. The available organizations are listed in the “repository owner” drop-down:
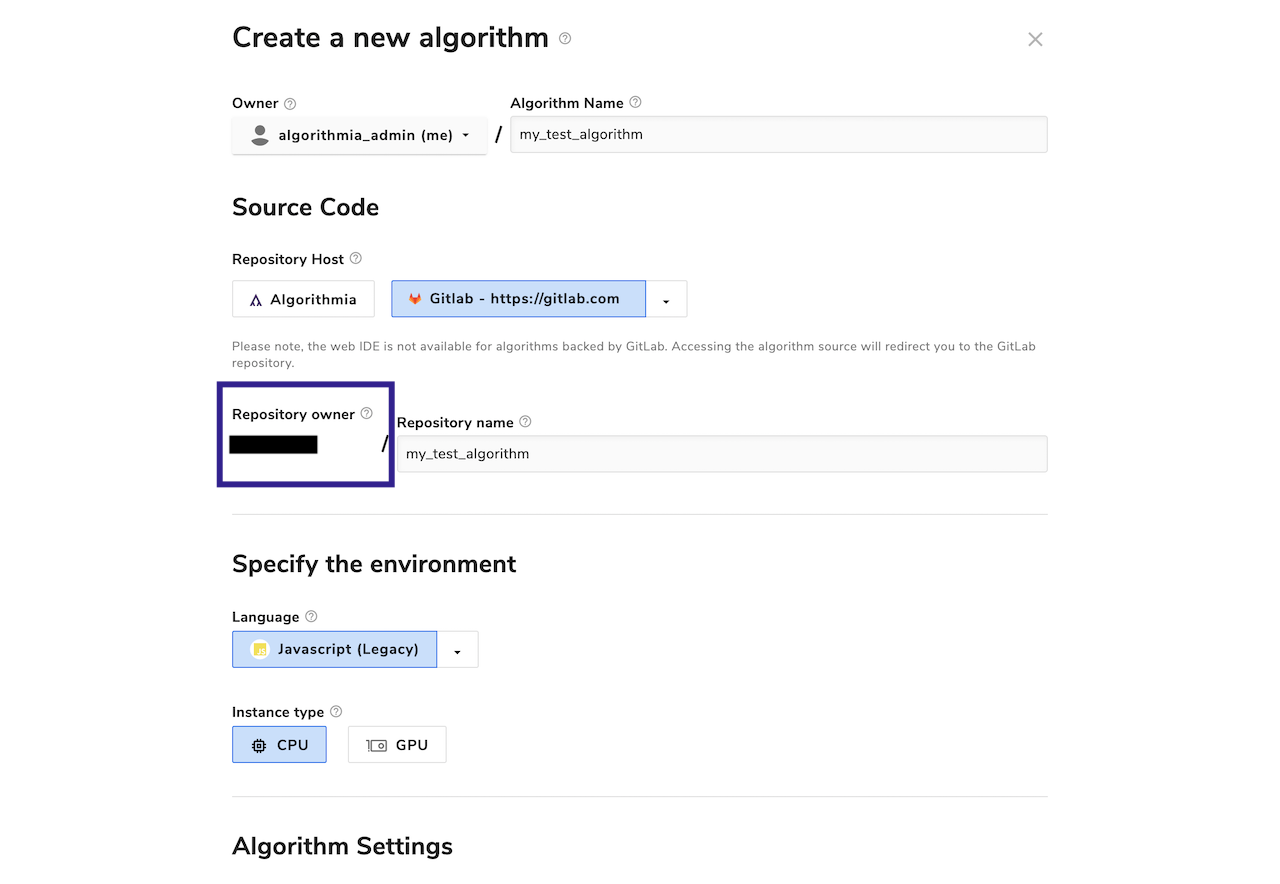
You may also customize the name of the repository that’s created. By default, it’ll be the name of your algorithm.
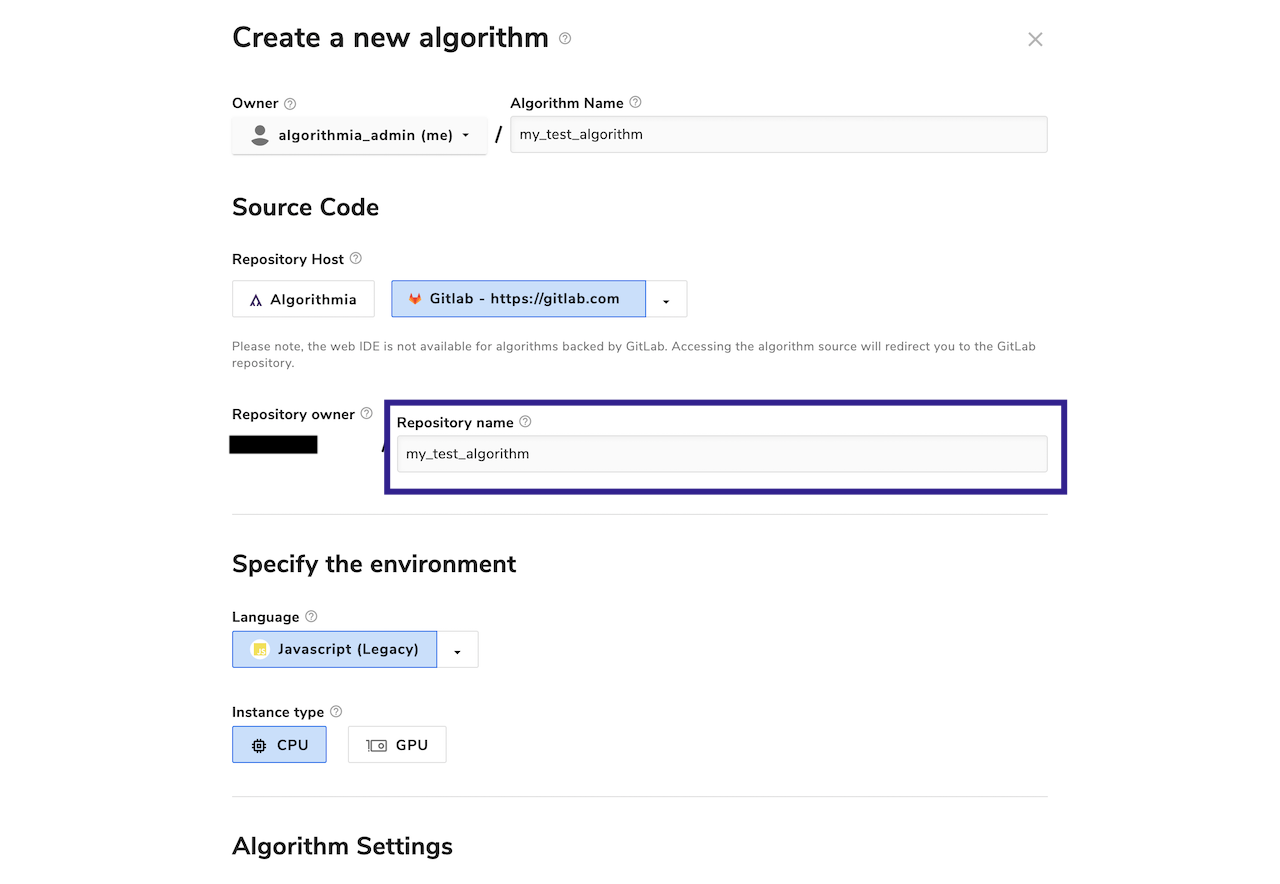
If you decide to use an alternative name, we recommend that you use only letters, numbers, hyphens, and/or underscores. While GitLab will accept characters outside this range, it will replace any unsupported characters with an underscore, potentially resulting in an undesired repository name.
When we create your repository, we associate the following with it:
- A Deploy Key: GitLab deploy keys allow read-only access to specific repositories, and are GitLabs’s prescribed means by which external services can fetch code for building and deploying. These keys are not tied to individual permissions, and as such will allow Algorithmia to continue building an algorithm even if the permissions of the creating user change. We also use deploy keys to obtain your repository’s commit log (to display changes when publishing versions) and README.md (for use as algorithm documentation).
- Webhooks: We set up webhooks to receive notifications about changes to your repo, such as when there’s a change to its default branch.
Updating GitLab-hosted algorithms
Once you’ve created your algorithm, any commits to your GitLab repository’s default branch will result in a build on Algorithmia. At creation, your repository’s default branch will be your master branch, but you can change this at any time in your repository’s settings.
You can view your algorithm’s builds by heading to its landing page and clicking the “Builds” tab if you are the algorithm’s owner.
Publishing GitLab-hosted algorithms
When you’re ready to create a new version of your algorithm, visit that algorithm’s page and select the “Builds” tab. Locate the build corresponding to specific commit SHA you wish to use, and then click “Publish” on the right side of the row.
This will open a publish modal that will let you publish your algorithm.
If you don’t see any builds listed, make sure that you’re pushing commits to your repository’s default branch. Builds are only triggered for commits pushed to the default branch.
To learn more about algorithm builds, click here.
Deleting GitLab-hosted algorithms
If you wish to delete an algorithm that hosts its source code on GitLab, have no fear—the repository will be left unharmed. If you do wish to destroy your algorithm’s source code, you can follow these instructions.
Managing your GitLab authorization
If you want to review your GitLab authorization status, you can visit your account settings page. Simply scroll to the “Source Code Management” section to view any prior GitLab authorizations, or to connect your account.
Troubleshooting GitLab-hosted algorithms
If we experience a temporary disruption in connectivity with GitLab, your source code will be unavailable for modification during the duration of that disruption. The following are some additional scenarios under which algorithm source code won’t be available, to help you troubleshoot.
Your repository’s deploy key was removed
We depend on deploy keys to pull source code from your algorithm for building. A deploy key is simply an SSH keypair with read-only access to a specific repository. Algorithmia securely stores the private key while the public key is shared with GitLab.
You can obtain the public key for your repository by navigating to your algorithm’s settings page and clicking “View Key”. You’ll be presented with a modal, from which you can copy the public key.
With the deploy key in hand, simply follow instructions outlined here to restore the public key to your repository.
Your repository was deleted
If your algorithm’s GitLab repository was deleted, GitLab does not have a mechanism for restoring easily without backups. It is essential that both the repository’s deploy key and webhooks remain in place, otherwise we will not be able to pull your source code, or know when you make changes.
Your repository’s webhook needs to be restored
We depend on webhooks to notify us of changes to your algorithm’s repository. To restore your webhook within GitLab, first locate the webhook URL and secret. This can be found under the “Settings” tab on your algorithm’s homepage in Algorithmia. Just click “View Details” under “GitLab Webhook”.
You’ll then be presented with a modal, from which you can copy the webhook URL and secret.
Once you’ve found these values, visit your algorithm’s repository on GitLab and click on the Settings tab. Click ‘Webhooks’ on the left side, and you’ll be able to restore your webhook by entering the webhook URL and secret.
FAQ
I’d like to reuse an existing GitLab repository for my algorithm. Is this possible?
At this time we are only able to use new, purpose-created repositories for GitLab-backed algorithms, which Algorithmia itself creates and provisions.
Can I rename or move the GitLab repository that backs my algorithm?
Yes! Upon any change to your repository’s name or owner we receive a webhook which we will use to update our system to point to the new repository address.
I revoked access to the Algorithmia’s GitLab OAuth application, and now none of the repositories I created can build!
When you revoke access to an OAuth app, GitLab automatically revokes both your token and any deploy keys you may have created via the OAuth app. To fix your algorithms, simply follow the instructions above on restoring deploy keys to a repository.
Hosting source code on Bitbucket Server
By hosting your algorithm’s source code on Bitbucket Server, you can take advantage of Bitbucket Server’s rich set of developer features, such as pull requests, and also ensure that access to your source code is carefully mediated.
If you haven’t used Git before, we recommend this Git tutorial series by GitHub.
Web IDE Support: At this time we don’t support editing source code in our Web IDE for BitBucket Server-hosted algorithms.
No OAuth Support: Bitbucket Server does not support OAuth, so a token-based flow is implemented to connect Bitbucket Server-hosted algorithms.
Enterprise Users: By default, on new Algorithmia clusters algorithm source code can only be hosted internally within the Algorithmia platform. As such, you won’t see Bitbucket Server listed as a repository host for new algorithms until your administrator creates a Bitbucket Server configuration.
Creating Bitbucket Server-hosted algorithms
To create an algorithm with its source code hosted on Bitbucket Server, simply select any available Bitbucket Server SCM configuration for “repository host” in the modal.
You can customize two aspects of any Bitbucket Server repository that’s created for an algorithm: the repository’s owner, and its name.
By default, all Bitbucket Server repositories are under a project configured by your cluster administrator. These projects are listed in the “repository owner” drop-down.
If you decide to use an alternative name, we recommend that you use only letters, numbers, hyphens, and/or underscores. While Bitbucket Server will accept characters outside this range, it will replace any unsupported characters with an underscore, potentially resulting in an undesired repository name.
When we create your repository, we associate the following with it:
- A personal access token: Bitbucket Server personal access tokens allow appropriate access to specific repositories, and are Bitbucket Server’s prescribed means by which external services can fetch code for building and deploying. These tokens are tied to individual permissions, and as such will not allow Algorithmia to continue building an algorithm if the permissions of the personal access token changes. We also use the personal access token to obtain your repository’s commit log (to display changes when publishing versions) and README.md (for use as algorithm documentation).
- Webhooks: We set up webhooks to receive notifications about changes to your repo, such as when there’s a change to its default branch.
Updating Bitbucket Server-hosted algorithms
Once you’ve created your algorithm, any commits to your Bitbucket Server repository’s default branch will result in a build on Algorithmia. At creation, your repository’s default branch will be your master branch, but you can change this at any time in your repository’s settings.
You can view your algorithm’s builds by heading to its homepage and clicking the “Builds” tab if you are the algorithm’s owner.
Publishing Bitbucket Server-hosted algorithms
When you’re ready to create a new version of your algorithm, visit that algorithm’s page and select the “Builds” tab. Locate the build corresponding to specific commit SHA you wish to use, and then click “Publish” on the right side of the row.
This will open a publish modal that will let you publish your algorithm.
If you don’t see any builds listed, make sure that you’re pushing commits to your repository’s default branch. Builds are only triggered for commits pushed to the default branch.
To learn more about algorithm builds, click here.
Deleting Bitbucket Server-hosted algorithms
If you wish to delete an algorithm whose source code is hosted on Bitbucket Server, have no fear—the repository will be left unharmed.
Managing your Bitbucket Server authorization
If you want to review your Bitbucket Server authorization status, you can visit your account settings page. Simply scroll to the “Source Code Management” section to view any prior Bitbucket Server authorizations.