This guide will walk you through setting up an algorithm to send messages to Azure Event Hubs (EH), Azure’s high-throughput data-streaming and event-ingestion service. Once configured, you can create workflows in which your algorithms publish data to an event hub, unlocking downstream storage, processing, and analytics capabilities on Azure.
Because Algorithmia doesn’t currently have a native Event Flows integration with Azure Event Hubs, you can use one of Microsoft’s official SDKs, for example the azure-eventhub Python client library or the azure-messaging-eventhubs Java client library to send and receive messages from within your algorithms. The workflow demonstrated here uses the Python SDK, which is available on PyPI, to send messages. To see our other message broker integrations, see Event Flows.
NOTE: Although we currently don’t support Azure Event Hubs natively for Event Flows, beginning in Algorithmia version 20.5.57 you can use Event Hubs as a message broker for Algorithmia Insights.
Event Flow configuration overview
The process of configuring Event Flows with an EH message broker involves multiple steps, some of which are to be completed on the Azure side and some of which are to be completed on the Algorithmia side. At a high level, the configuration steps are:
- On Azure, create an Event Hubs namespace and an event hub within it.
- On Algorithmia, create an algorithm to publish messages to the event hub and add the event hub’s secret connection string to the algorithm’s Secret Store.
- Test the connection by calling the algorithm with sample input.
1. Configuring resources in the Azure Portal
NOTE: The steps in this section are to be completed within the Azure Portal.
Creating an Event Hubs namespace and an event hub
NOTE: If you’re familiar with the Apache Kafka platform, it can be helpful to understand the name mapping between Kafka and Event Hubs. In simple terms, an Event Hubs namespace is analogous to a Kafka cluster, and an event hub is analogous to a Kafka topic.
To begin, create an event hub using the Azure portal or using the Azure CLI. This will entail first deploying an Event Hubs namespace and then creating an event hub within the namespace. Because we’ll be sending messages using the Python SDK directly from an algorithm and not natively through Algorithmia’s internal infrastructure, the event hub can exist in any Azure account to which you have access. In other words, the Azure account in which the event hub is created doesn’t need to be the account running the Algorithmia platform, and no additional permission-configuration steps are required.
Gathering required parameters
When the resource deployment described in the links above is complete, click on the name of the resource group into which the namespace was deployed. You can filter by event hubs namespace to see the newly created namespace resource.
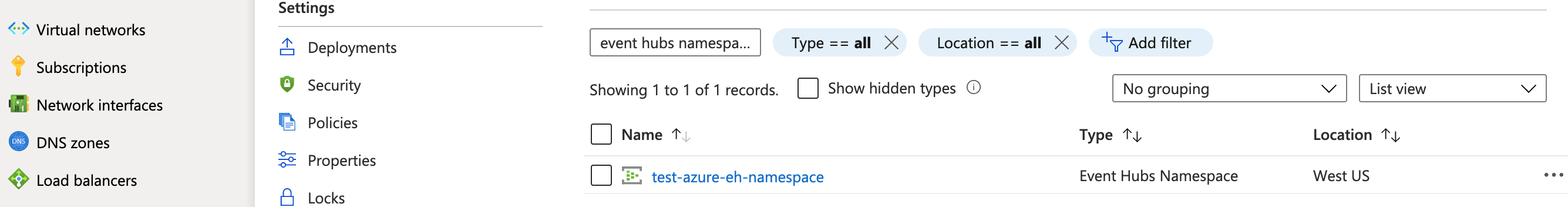
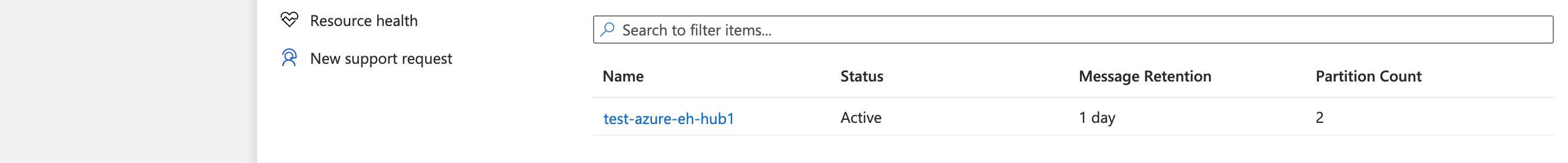
If you click into the namespace, you’ll see the event hub listed at the bottom. In the algorithm code below, you’ll replace this event hub name as the EVENTHUB_NAME value.
On the namespace page, from the left-hand navigation submenu under Settings, select Shared access policies and click on the RootManageSharedAccessKey policy.
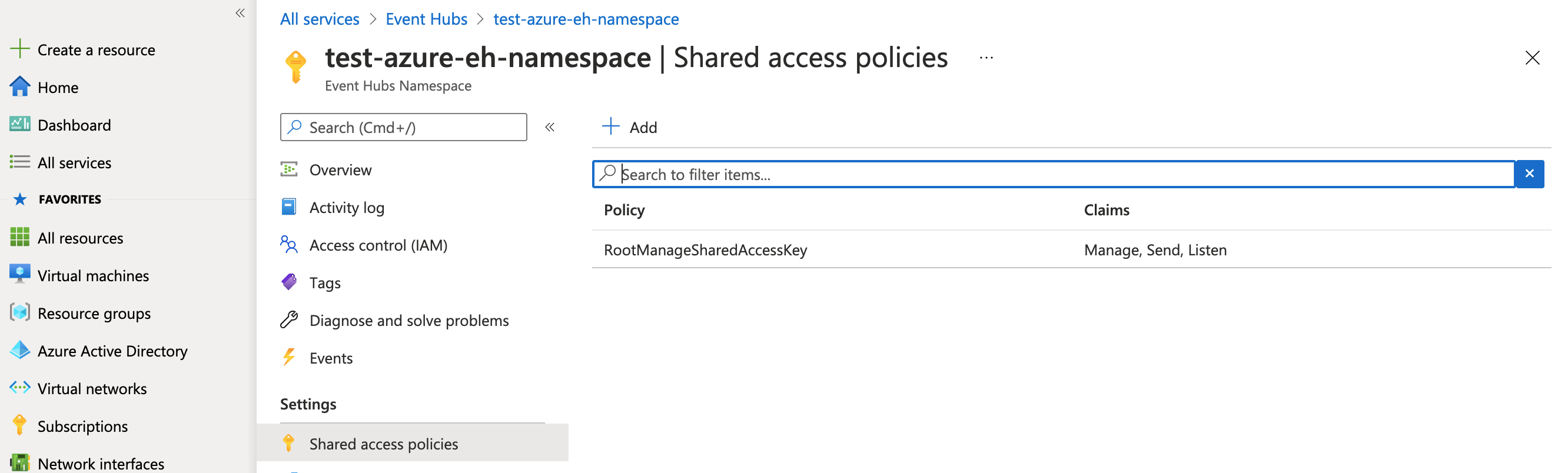
In the fly-out menu at right, copy the Connection string–primary key. This connection string enables your algorithm to communicate with Event Hubs. In the next step, you’ll save this string value in your algorithm’s Secret Store and access it from the code below as the CONNECTION_STR environment variable. Note that this is the connection string associated with the Event Hubs namespace, not the event hub itself. The value will look something like:
Endpoint=sb://test-azure-eh-namespace.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=RootManageSharedAccessKey;SharedAccessKey=+FehbdIzXYc6Hk2sckMuX0iTfLV4wWuZMkCGeNImi6s=
2. Creating an Event Hubs publisher algorithm in Algorithmia
NOTE: The steps in this section are to be completed on Algorithmia, from within the browser user interface (UI) or through the API.
As noted above, in this workflow we’re using Microsoft’s azure-eventhub Python SDK to send messages to EH from within an algorithm. For more information on how to use this library to send and receive messages, see Microsoft’s Quickstart Guide.
Create an algorithm
To begin create a Python 3.x algorithm with a generic Python 3.7 algorithm environment and default settings. If you’re new to Algorithmia or need a quick refresher on how to create and modify algorithms, see our Getting Started Guide.
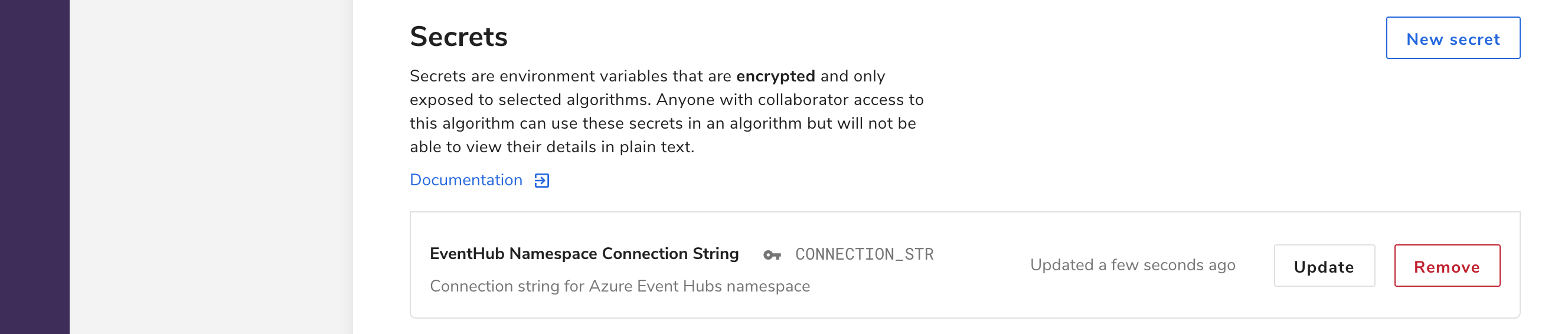
Store the connection string in the Secret Store
On the newly created algorithm’s profile, click the Settings tab and find the Secret Store section. Add a new secret called CONNECTION_STR with the contents of the connection string from above. For more information on how to use the secret store, see the Secret Store docs.
Modify, build, and publish the algorithm
Click the Dependencies button and add the Azure Event Hubs package, which Algorithmia will pull down automatically from PyPI when the algorithm is built. (If developing locally, you’ll add this to the requirements.txt file.)
algorithmia>=1.0.0,<2.0
azure-eventhub==5.6.0
In the body of your algorithm, paste the source code below, replacing the EVENTHUB_NAME value as described above.
import asyncio
import os
import Algorithmia
from azure.eventhub.aio import EventHubProducerClient
from azure.eventhub import EventData
# Event Hubs *namespace* connection string
CONNECTION_STR = os.getenv("CONNECTION_STR")
EVENTHUB_NAME = "EVENTHUB_NAME"
def apply(input):
"""Send messages to Azure Event Hubs.
input format: {"events": ["first event", "second event", "..."]}
"""
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(run(input))
return f"Sent event batch to Azure event hub '{EVENTHUB_NAME}'"
async def run(input):
# Create a producer client to send messages to the event hub.
# Specify a connection string to your event hubs namespace and
# the event hub name.
producer = EventHubProducerClient.from_connection_string(
conn_str=CONNECTION_STR,
eventhub_name=EVENTHUB_NAME)
async with producer:
# Create a batch.
event_data_batch = await producer.create_batch()
# Add events to the batch.
for event in input.get("events"):
event_data_batch.add(EventData(event))
# Send the batch of events to the event hub.
await producer.send_batch(event_data_batch)
Click the Save and Build buttons, and then Publish the algorithm.
3. Sending messages to the broker
To send a test message, call the algorithm with input in the following format.
{"events": ["first event", "second event", "..."]}
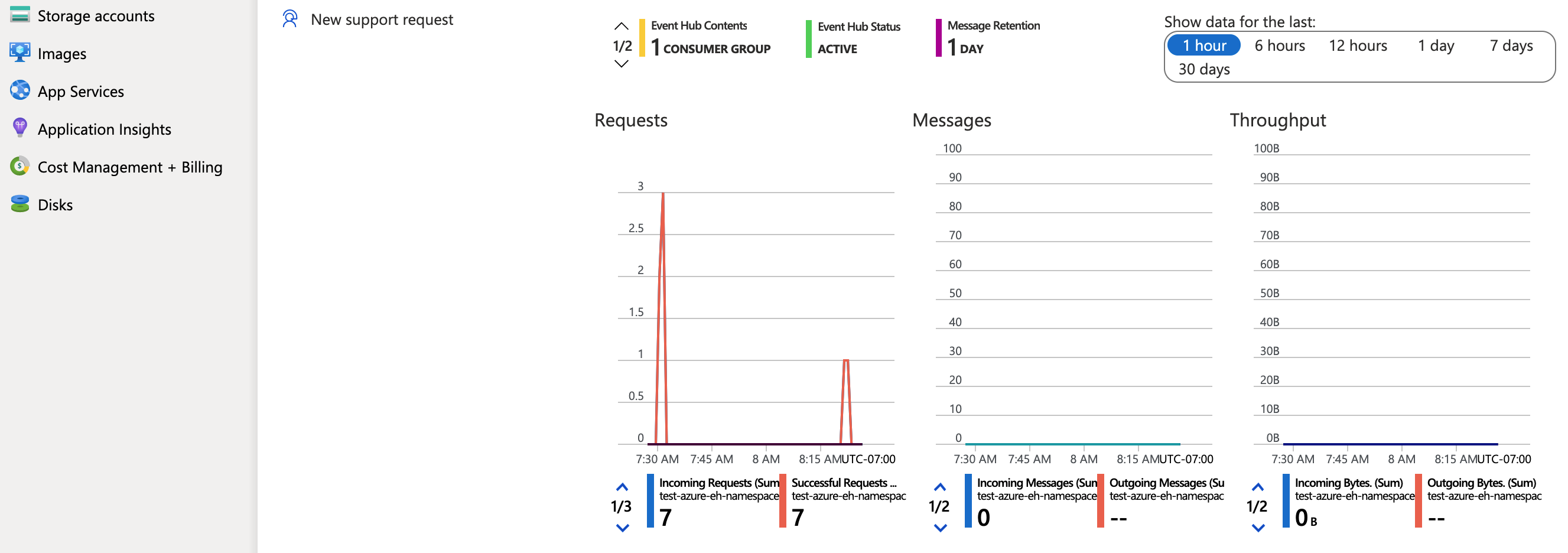
If you now click into the event hub in the Azure Portal, you’ll be able to see that it’s receiving messages from the algorithm.